Breathtaking What Is Redox Reaction

A redox reaction is the force behind an electrochemical cell like the Galvanic cell pictured.
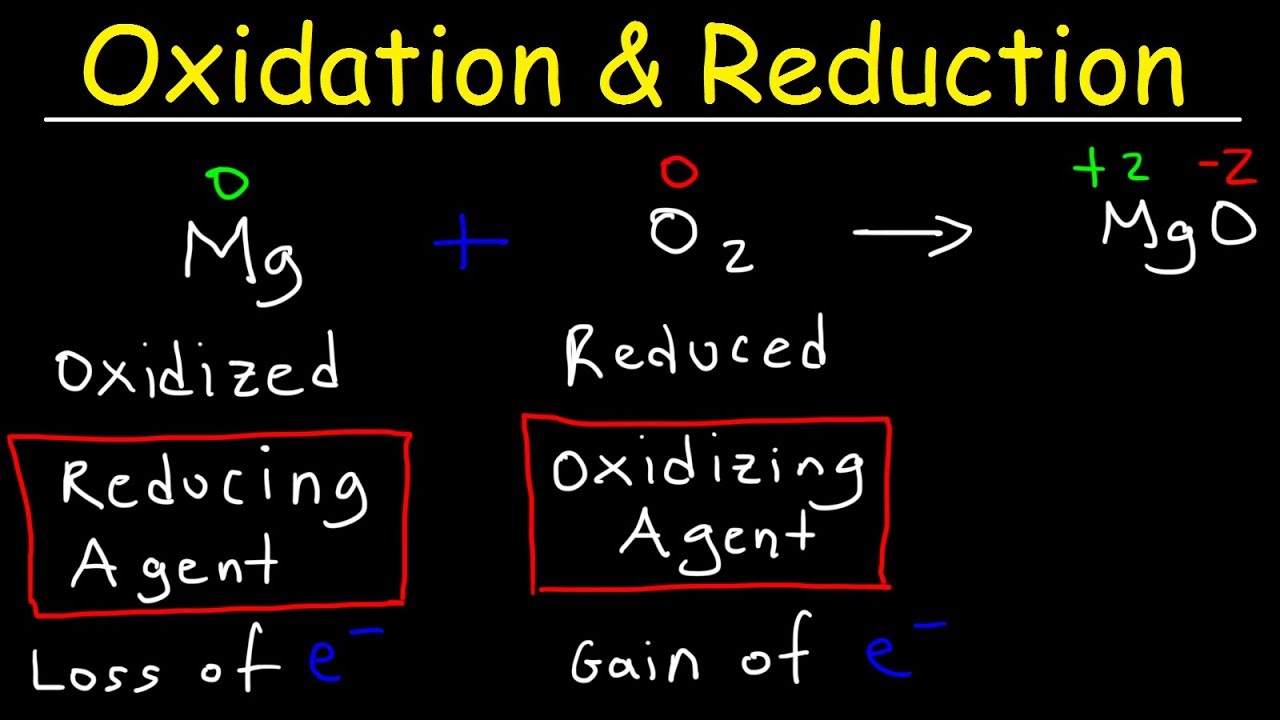
What is redox reaction. Based on these values mark the correct statement. Oxidation involves loss of electrons and increases in the oxidation state whereas reduction involves the gain of. Therefore redox reaction is also known as oxidation-reduction reaction.
A reduction-oxidation or redox reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which reduction and oxidation occur at the same time. State of the species involved must change. The battery is made out of a zinc electrode in a ZnSO 4 solution connected with a wire and a porous disk to a copper electrode in a CuSO 4 solution.
The most energy efficient initiation methods are based on bimolecular redox reactions which can be carried out under mild conditions and without any additional energy source2 One of the oldest redox system for the generation of free radicals is Fentons reagent. These reactions are important for a number of applications including energy storage devices batteries photographic processing and energy production and utilization in. Redox Reactions The reduction is the gain of electrons whereas oxidation is the loss of electrons.
Redox reactions are chemical reactions involving oxidation and reduction occurring simultaneously. The copper metal will dissolve and zinc metal will be deposited Answer. Like acidbase reactions oxidants accept protons and reductants donate electrons.
Redox reactions are reactions in which one species is reduced and another is oxidized. An oxidation-reduction redox reaction is a type of chemical reaction that involves a transfer of electrons between two species. Characteristics of redox reactions.
Redox reduction-oxidation reactions are those in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Reactions involving electron transfers are known as oxidation-reduction reactions or redox reactions and they play a central role in the metabolism of a cell. 031 - Redox ReactionsIn this video Paul Andersen explains how redox reactions are driven by the movement of electrons from the substance that is oxidized to.