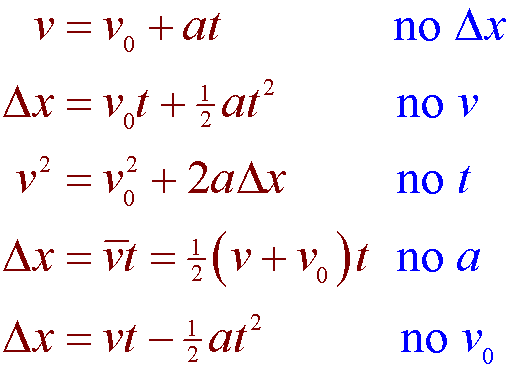Fantastic Velocity Kinematic Equation

To find the position equation simply repeat this step with velocity.
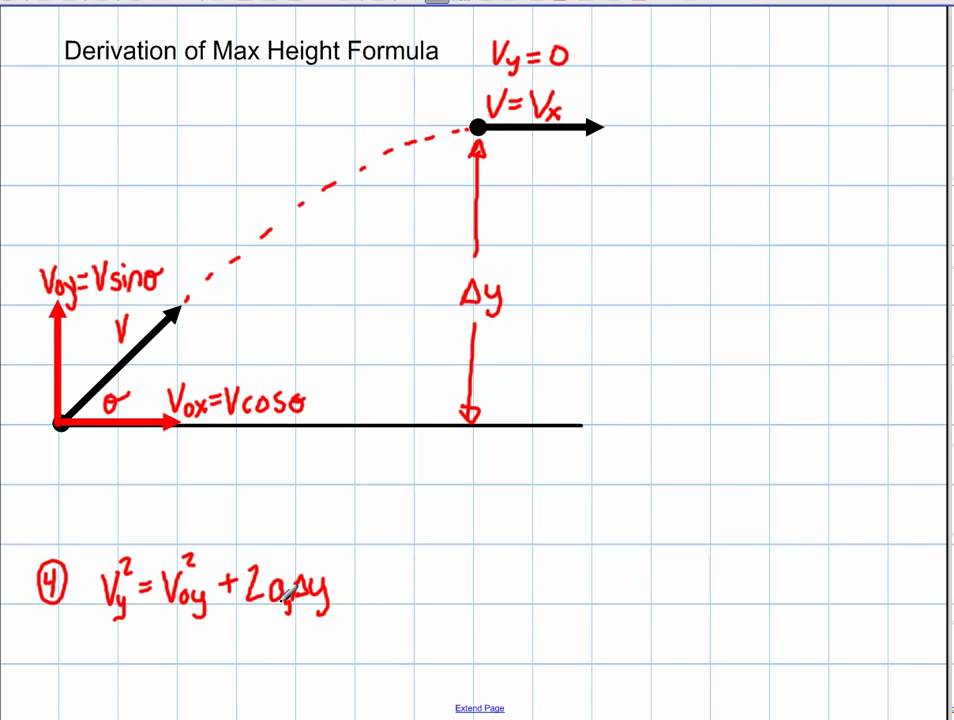
Velocity kinematic equation. V f Final velocity. Simplifying the integral results in the equation v t -98t C_1 where C_1 is the initial velocity in physics this the initial velocity is v_0. V f 2 V f 2 2aD.
V f v i at The substitution and algebra are shown here. Average velocity equals the slopeof a position vs time graph when an object travels at constant velocity. There are four kinematic equations which associate with Displacement Velocity Time and Acceleration.
This equation can only be used when acceleration is constant. Nikravesh 3-2 Velocity equations The time derivative of the position equations yields the velocity equations. Vecv vecu vecat Learn more about Relative Velocity Motion in.
This means that for every second the velocity decreases by -98 ms. L 2 sinθ 2ω 2 L 3 sinθ 3ω 3 R BO 2 0 L 2 cosθ 2ω 2 L 3 cosθ 3ω 3 0 sc1v1 These equations can also be represented in matrix form where the terms associated with the. The derivative of velocity with time is acceleration a dv dt.
The equations can be utilized for any motion that can be described as being either a constant velocity motion an acceleration of 0 mss or a constant acceleration motion. Because kinematics equations are used when the acceleration of the object is constant we can use a simple equation to determine the average velocity of an object. Constant velocity Average velocity equals the slope of a position vs time graph when an object travels at constant velocity.
Kinematic equation formula Questions. Or integration finding the integral The integral of acceleration over time is change in velocity v a dt. V romega qquad a_c -romega2 qquad a ralpha v rω ac rω2 a rα.