Brilliant Curved Arrow Notation
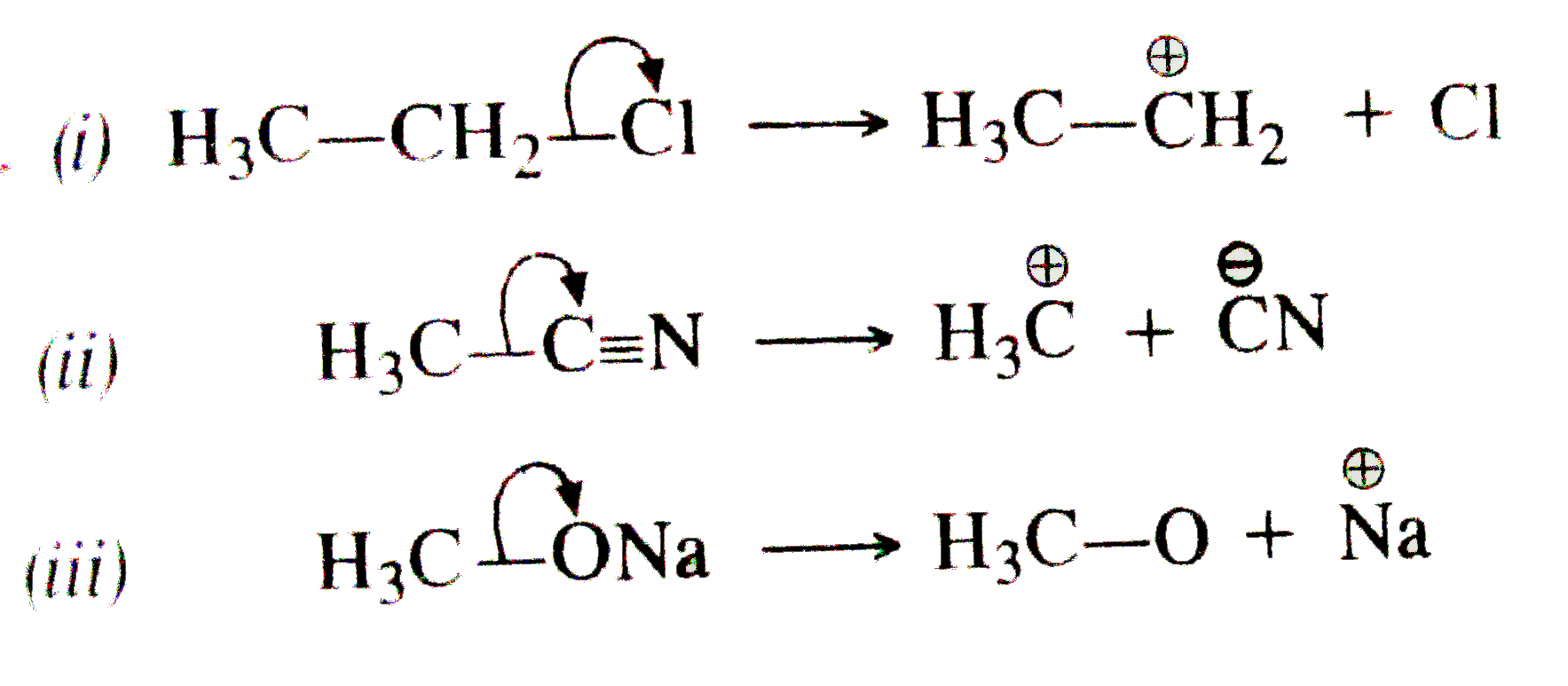
What is curved arrow notation explain with example.
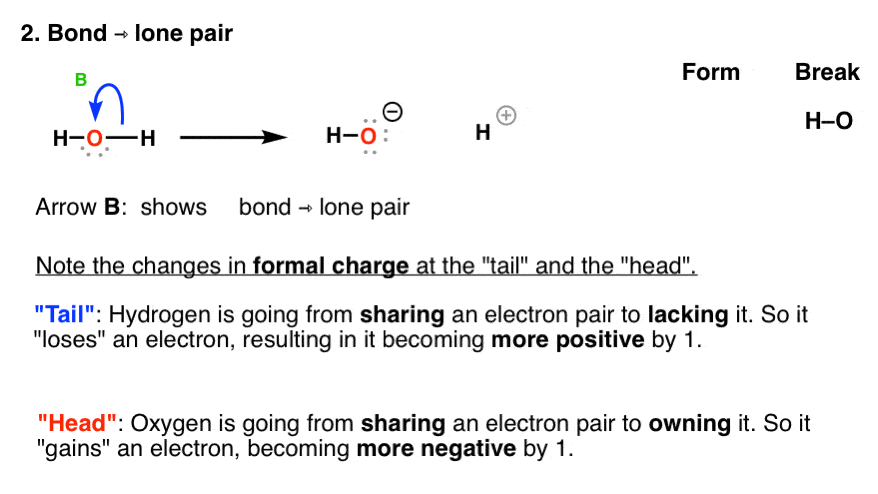
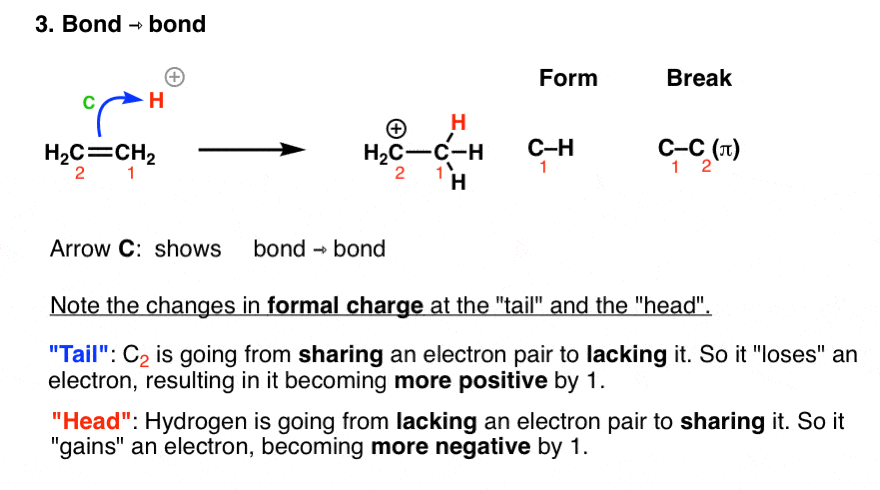
Curved arrow notation. Curved arrows indicate electron flow. In using arrow pushing curved arrows or curly arrows are superimposed over the structural formulae of reactants in a chemical equation to show the reaction mechanism. Since a pair of electrons are being donated from the tail the atom at the tail will have a formal loss of one electron making its charge more positive by 1.
A single barbed arrow represents one electron and a double barb represents two electrons. Curved arrows are also a way of tracking changes in formal charge. These electron reorganizations can be shown by the use of curve arrows.
The head of the arrow is placed at the destination of the electrons. Most organic transformations involve the reorganization of electrons from one bonding pattern to another. Curved Arrows Also Represent A Way of Tracking Changes In Formal Charge.
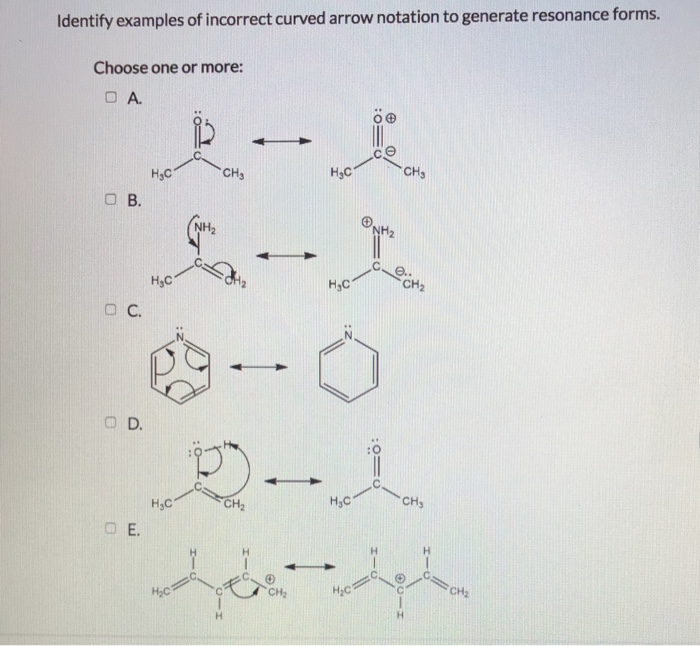
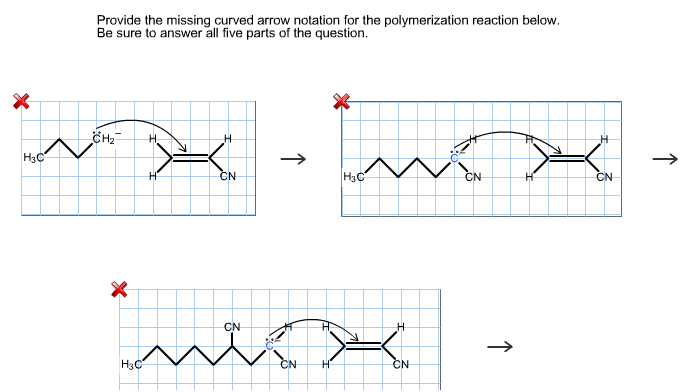
Using the curved - arrow notation show the formation of reactive intermediates when the following covalent bonds undergo heterolytic cleavagea. Complete the mechanism for the intramolecular aldol reaction shown below. Curved Arrow Notation Curved arrows or curved arrows notation is a very powerful tool you will learn in organic chemistry.
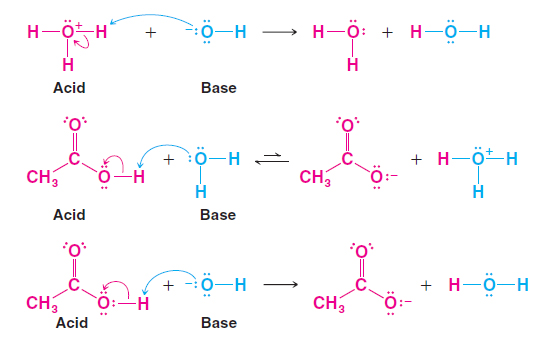
-Acid B-H Acid Use curved arrows to show the proton transfer mechanism of the following reactions. This makes it easier to keep track of the bonds forming and breaking during the reaction as well as visualizing and explain more advanced features. The reaction requires a base eg NaOH but we will ignore the Na because it does not participate in the mechanism.
The base of the curved arrow is placed at the source of the electrons that are moving. From this stems the ability to predict reaction products and mechanisms beyond the realm of memorization. The arrows illustrate the movement of electrons as bonds between atoms are broken and formed.