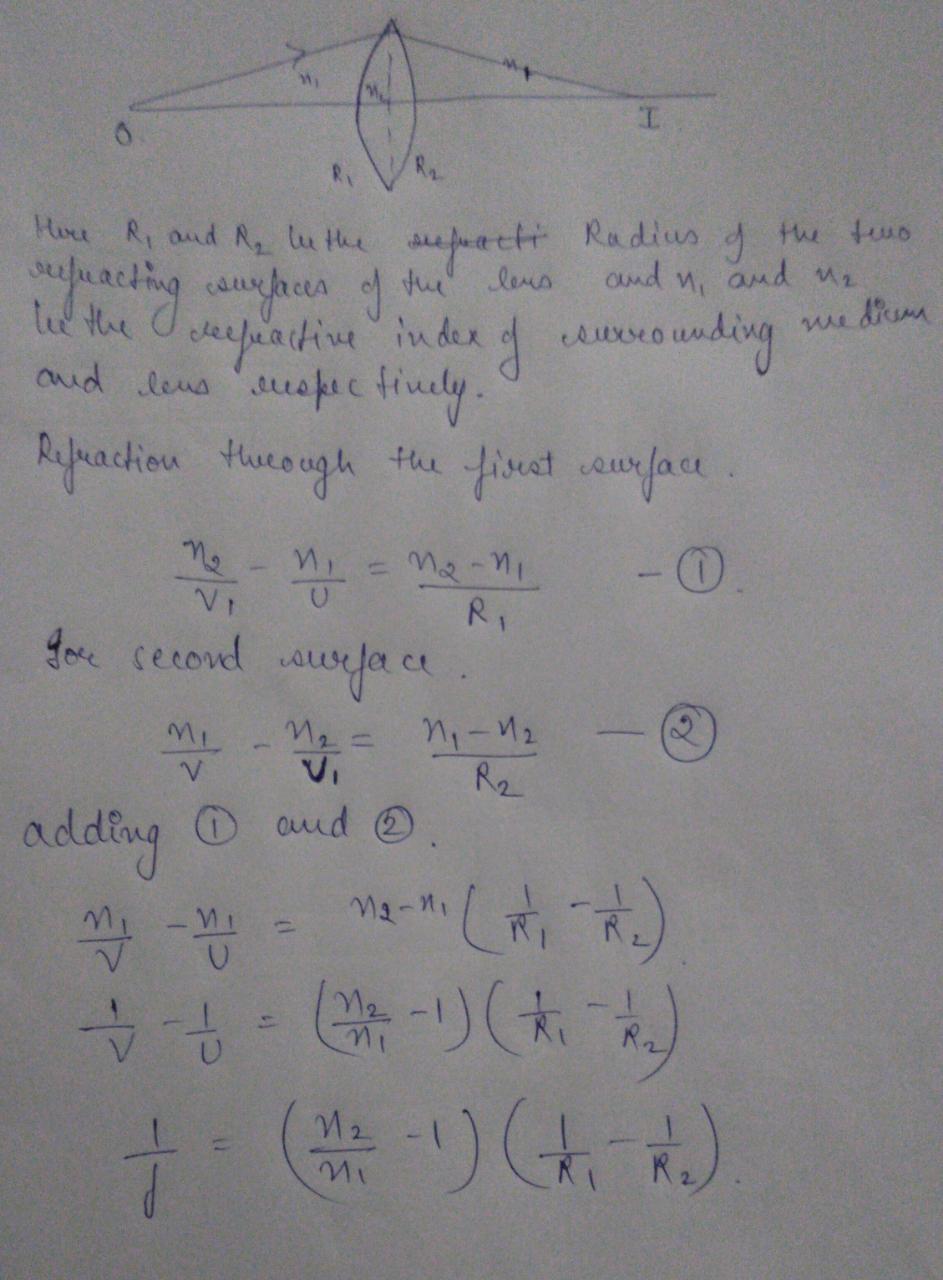Great Lensmaker Equation Derivation

Equation 13 is called the lensmakers equation.
Lensmaker equation derivation. A number of idealizations simplifications and approximations are used to complete the derivation but the results are compact and sufficiently accurate for. Derivation of the laws of reflection and refraction. So to derive the lens makers formula you first need to derive the relation between object and image distance in terms of refractive index of the medium and the radius of curvature of the curved spherical surface.
Derivation Of Lens Maker Formula Lenses of different focal lengths are used for various optical instruments. 1 f n L n m 1 1 R 1 1 R 2 n L n m 1 d n L R 1 R 2 However I can not find any derivation of it online. What is its focal length when immersed in water n 133.
A lens maker formula may be defined as the formula which gives the relationship for calc. 1 For a lens of index n g surrounded by two different media n 1 and n 2 1 f Φ Φ S 1 Φ S 2 Φ S 1 Φ S 2 d n g Per Gullstrands equation with respect to principal planes. The focal length of a lens depends upon the refractive index of the material of the lens and the radii of curvatures of the two surfaces.
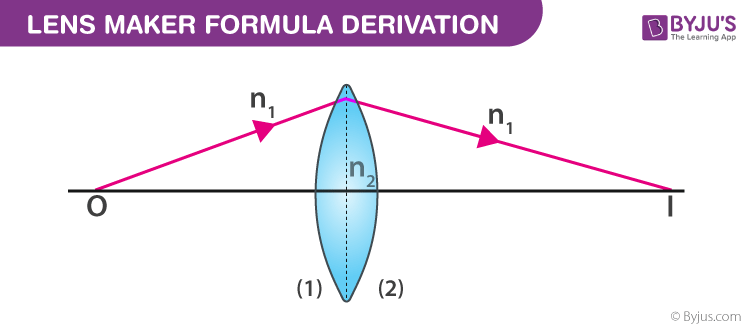
Its not mandatory but it makes the derivation. The lensmakers formula relates the index of refraction the radii of curvature of the two surfaces of the lens and the focal length of the lens. In this video learn how to derive lens maker formula for thin lens.
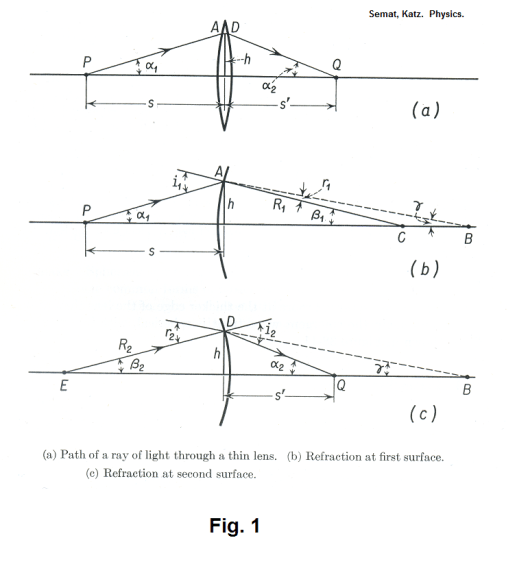
Deriving the Lensmakers Equation Level 4 The Lensmakers Equation links the radii of curvature of two sides of a lens the refractive index of the material from which it. The above figure is Figure 25 p. The well-known equation for thin lens is.
The lensmakers equation relates the focal length of a simple lens with the spherical curvature of its two faces where and represent the radii of curvature of the lens surfaces closest to the light source on the left and the object on the right. SF017 SF027 51 15 Thin Lenses Formula and Lens makers Equation Considering the ray diagram of refraction for 2 spherical surfaces as shown in figure below. 1 f n L n m 1 1 R 1 1 R 2 But theres a more appropriate equation that includes the thickness of the lens which is.