Breathtaking How To Find The Instantaneous Acceleration
S 5 t3 - 3 t2 2t 9 v 15 t2 - 6t 2 a 30t - 6 If we want to know the instantaneous acceleration at t 4 then a 4 30 4 - 6 114 m s2.
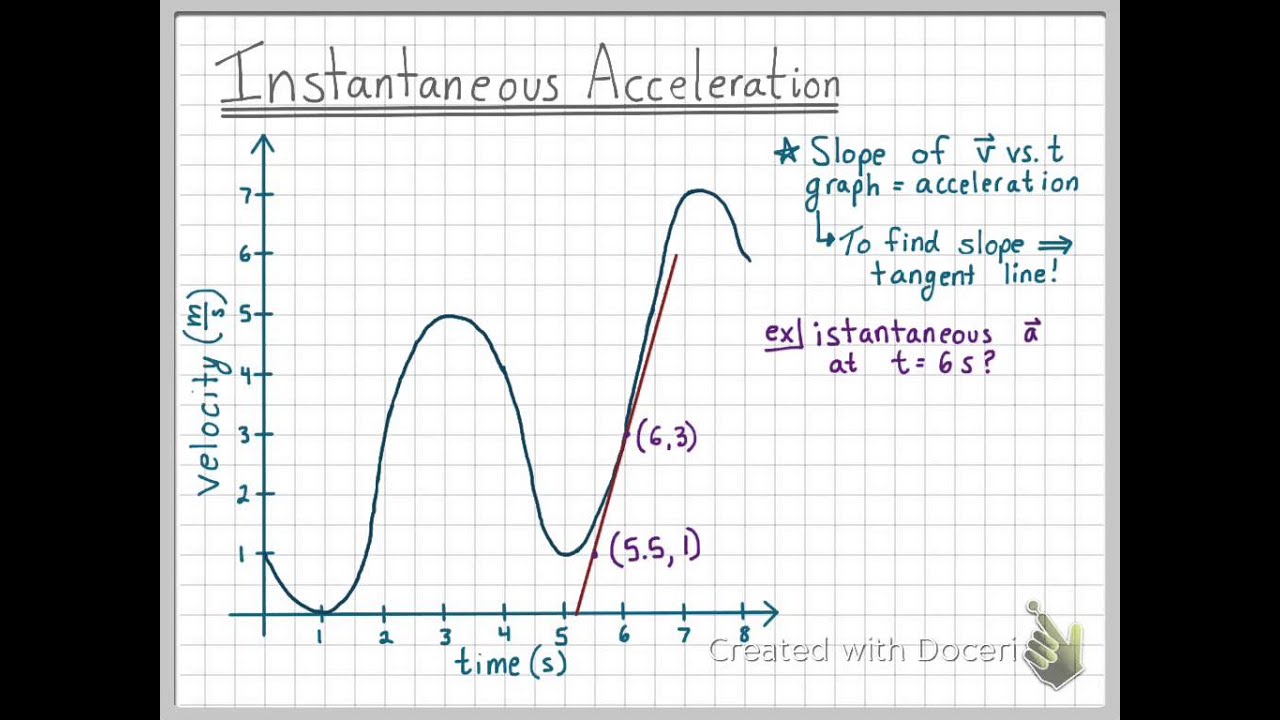
How to find the instantaneous acceleration. Thus similar to velocity being the derivative of the position function instantaneous acceleration is the derivative of the velocity function. I need to find the acceleration at a specific time for example 6s. The most useful part of this line is that students can tell when the velocity is increasing decreasing positive negative and zero.
Instantaneous acceleration a or acceleration at a specific instant in time is obtained using the same process discussed for instantaneous velocity. Take the velocity vector a two points separated by an infinitesimally small time interval. As said earlier above this Δt has to be near zero if.
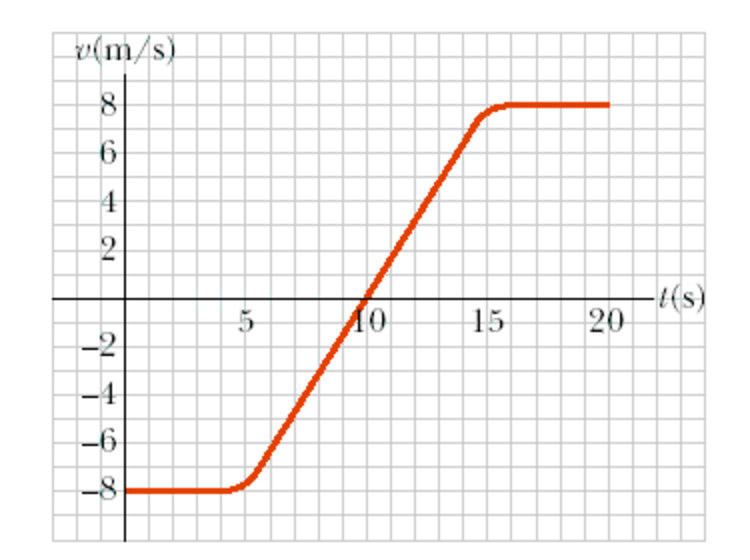
How do you find instantaneous velocity from acceleration. If your graph looks curvy--not just made out of straight lines the slope will be changing which also means velocity is changing and it implies acceleration. G 3-00-6 3-6.
That is we calculate the average velocity between two points in time separated by Δ t and let Δ t approach zero. Thus similar to velocity being the derivative of the position function instantaneous acceleration is the derivative of the velocity function. The Instantaneous Velocity is articulated in ms.
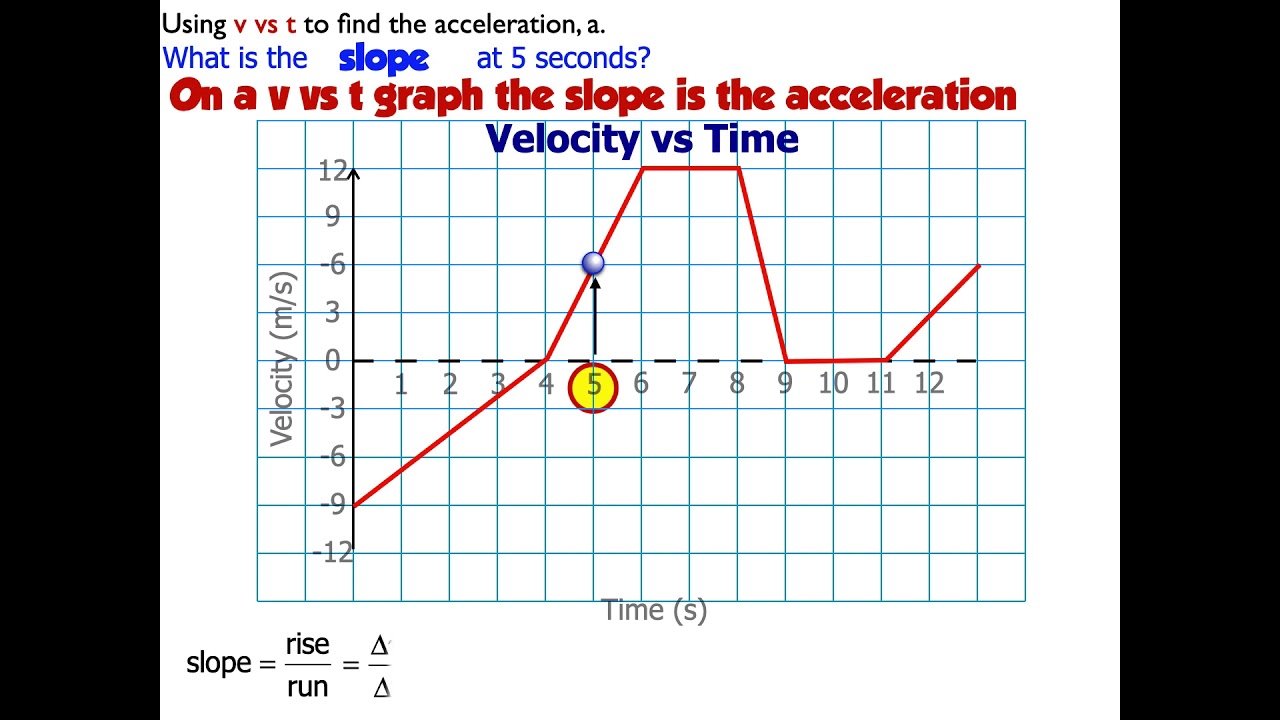
It is explained as the limit of the average acceleration in which the total time is considered to reach zero. How to calculate the instantaneous acceleration from a velocity vs time graph. Vt V0 T a Where Vt is the instantaneous velocity.
Definition Formula and more. How to calculate the instantaneous acceleration from a velocity vs time graph. That is we calculate the average velocity between two points in time separated by Δt Δ t and let Δt Δ t approach zero.